Power Up! The Fascinating Journey of Phone Chargers
Intro:
Let’s face it — our phones are basically our lifelines. But what keeps those lifelines alive? Chargers! Those silent heroes have come a long way from clunky bricks to sleek slabs of magic. So, plug in (or don’t, if you’re into wireless) and join us on a fun trip through the electrifying world of charging evolution.
The Early Days: One Charger to (Only) Charge One Thing
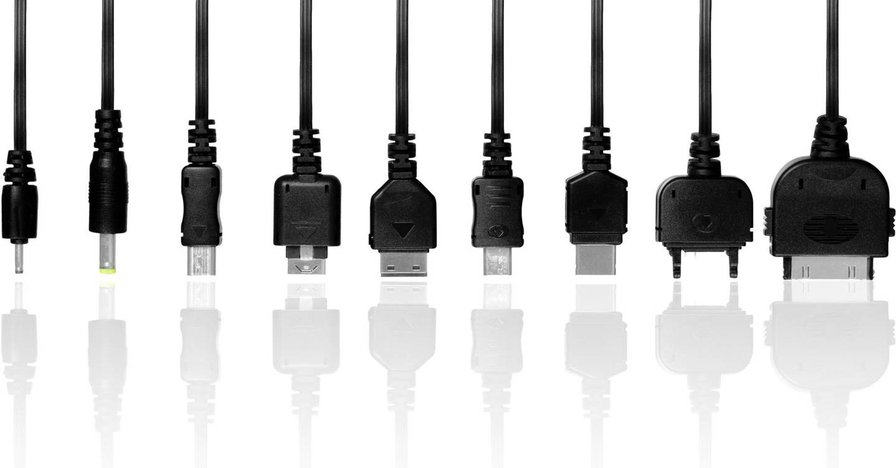
Back in the early 2000s, chargers were not created equal. Every phone had its own chunky plug. Nokia? Fat round pin. Sony Ericsson? Weird rectangle thing. Lose your original charger? Good luck.
They were heavy, slow, and forget about “fast” — charging your phone overnight was the norm.

Enter the “Universal” Charger (Kind of)
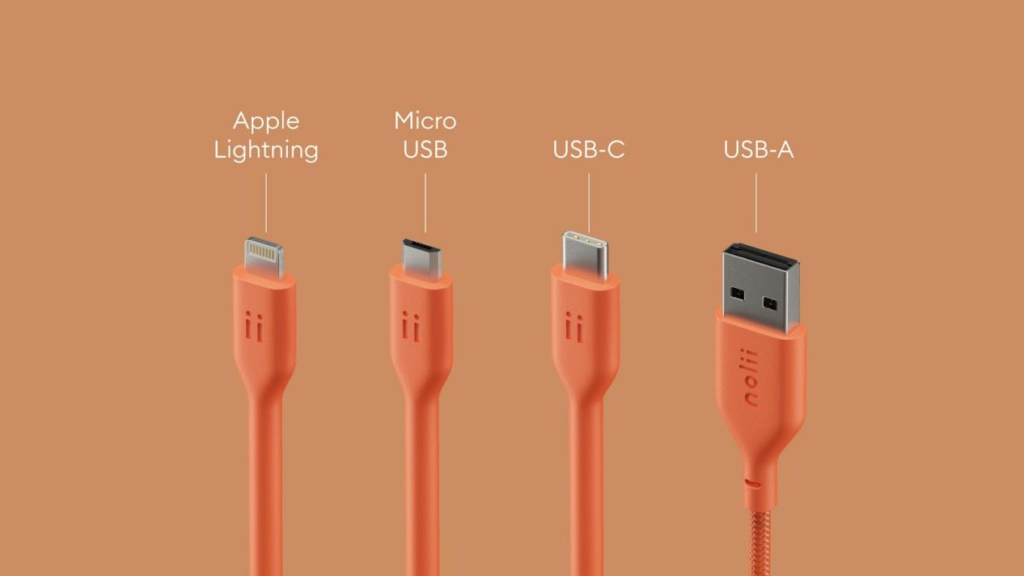
Then came micro USB, and suddenly, things felt more civilized. One cable to rule most gadgets — phones, cameras, Bluetooth headsets. But “universal” was still a lie — Apple stuck to its own Lightning cable, and laptops? Still in their own dinosaur league.
This era also gave birth to the “universal charger” — remember those odd boxes with interchangeable heads and voltage switches? They looked more like science projects, but hey, they worked (most of the time).

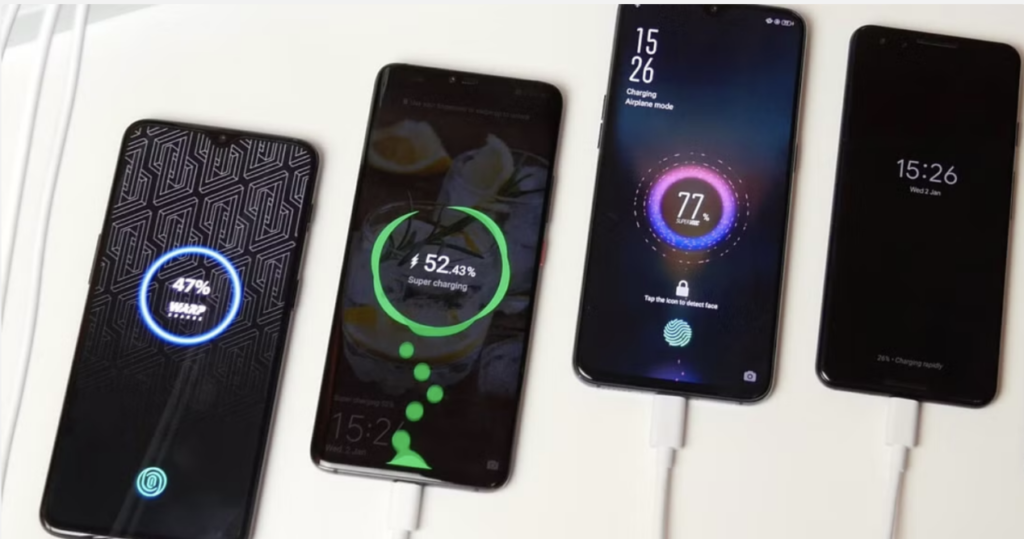
Fast Charging: Because Who Has Time Anymore?
Then came fast charging, and life changed forever. What used to take hours now takes minutes. Technologies like Qualcomm’s Quick Charge, OPPO’s VOOC, and USB Power Delivery (PD) turned our phones into caffeine-fueled sprinters.
You could literally plug in your phone, take a shower, and come back to 80% battery. That’s not charging — that’s wizardry.

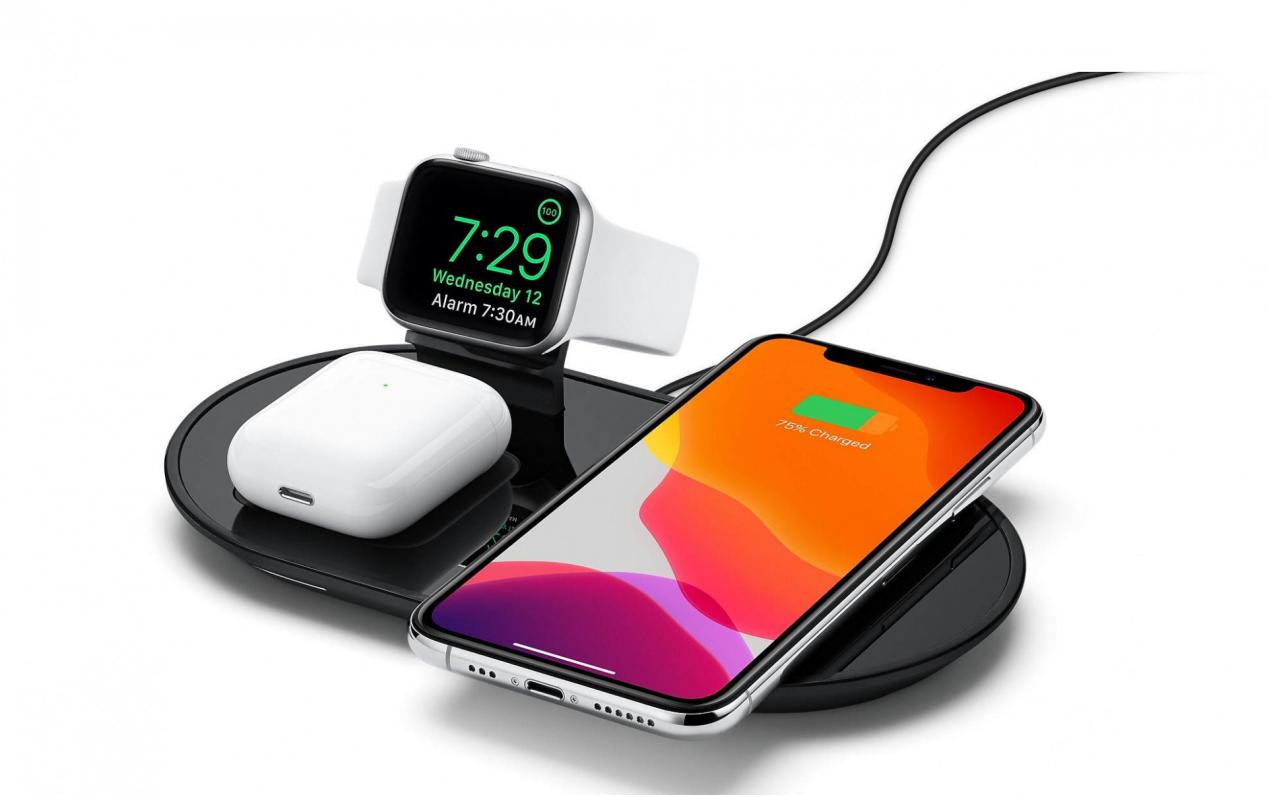
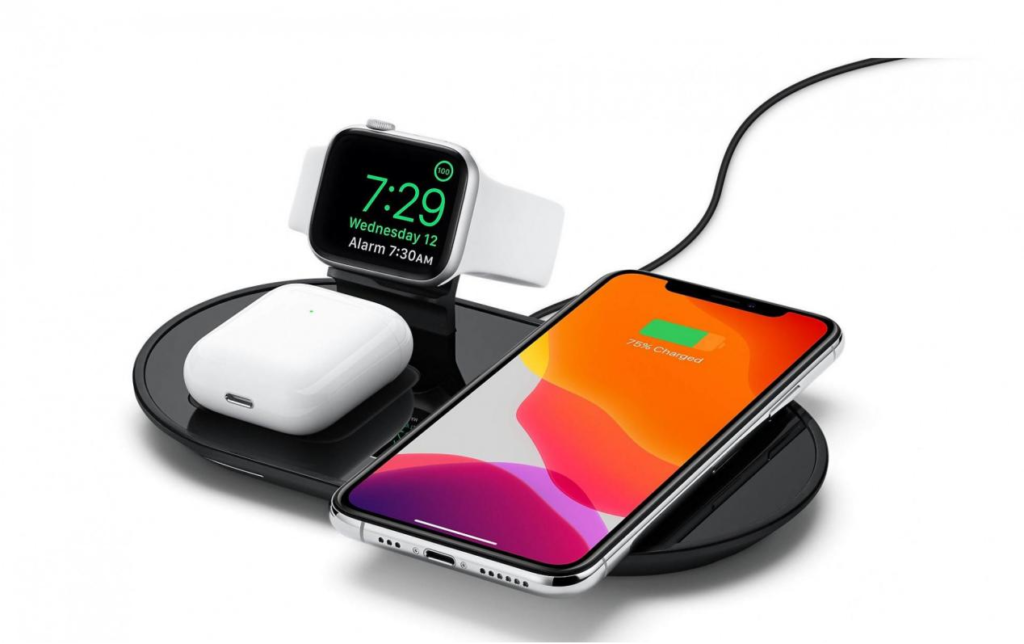
Wireless Charging: The Magic Carpet Ride
At first, wireless charging felt like sci-fi. Just place your phone on a pad and watch the battery go up? What is this, Hogwarts?
Of course, early wireless charging was more like “slow-less charging,” but recent upgrades like MagSafe, Qi 2.0, and reverse wireless charging (yes, your phone can now charge other gadgets) made it genuinely practical.
No more cable clutter. Just sleek, smooth surface vibes.

The Rise of the “One Charger to Rule Them All”
In 2025, we finally have multi-port, high-wattage, intelligent chargers that can power your phone, laptop, smartwatch, and toothbrush — all at once. GAN (Gallium Nitride) chargers made them smaller, cooler (literally), and more efficient.
The best part? These universal fast chargers actually deserve the name now.

What’s Next?
Imagine charging your phone through the air — no pads, no cables, just pure invisible energy. Companies are already experimenting with over-the-air charging using radio frequencies or laser beams. It’s still early days, but the future is charging up fast.
Conclusion:
From tangled wires to wireless wonders, the evolution of chargers is proof that even the most ordinary things can become extraordinary. So next time you plug in (or tap down), take a moment to appreciate the tiny piece of tech that’s keeping your digital life alive.
Charge on, folks. ⚡